
Freshman

Sophomore
Junior

Are you an early adopter? Do you like solving theoretical and practical problems using mathematics, logic, research and your own creative mind? Do you want to gain a deeper understanding of programming, software design, operating systems, and cyber technology in general? Are you ahead of the curve when it comes to understanding the profound impact technology can have on people’s lives? Do you want to be part of a trailblazing sector that will help find solutions and innovations that will positively change Central Asia and make the world a better place?
Apply now for UCA’s Computer Science programme, which will develop you into a stellar programmer, groundbreaker and future-ready information technology professional. The programme, taught by experienced and renowned faculty, will equip you to be part of the region’s new generation of tech specialists who will develop infrastructure, generate entrepreneurial opportunities, energize the economy and create a new vision for the future.
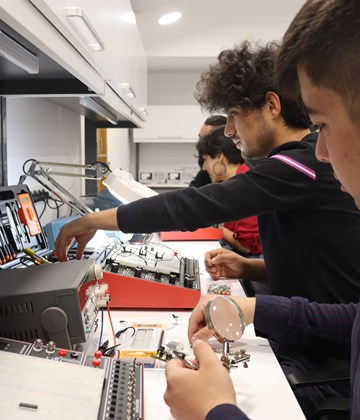
UCA’s Computer Science programme provides an innovative curriculum that equips students with a strong foundation in computational thinking, programming, and problem-solving, preparing them to shape the future of technology. Blending theory with hands-on experience, the curriculum covers key areas such as software development, data science, artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, blockchain, data structures and algorithms, computer architecture and networks, operating systems, and mobile app development. Students gain real-world skills through innovative projects, internships, and research opportunities. Students can use state of the art laboratories including hardware, IoT, computer and networking labs to experiment both hardware and software development. Graduates are well-prepared for dynamic careers in tech-driven industries or for advanced studies in specialised fields, making the program a launchpad for tomorrow’s digital leaders.
Core Curriculum* |
Specialised Courses |
|
Programming I Programming II Calculus I Calculus II Data Structure and Algorithms Digital Logic Design Computer Networks Web Technologies Operating Systems Information Technologies Introduction to Computer Science Computer Architecture Database Systems Programming Methodologies Software Engineering Compiler Design Android Application Design Computer Graphics Information Security Safety Management |
Microcontrollers Computer Systems Distributed Systems Computer Vision Object Oriented Programming Web and Internet Technologies Artificial Intelligence Cyber Security Blockchain Modelling and Simulation Automata Theory Internet of Things Machine Learning Mobile App Development Design and Analysis of Algorithms
|
* Courses are subject to change.
Elective courses are offered to students in line with national requirements, and students can also choose free elective courses from another major.
The programme turns students into widely educated, articulated, and knowledgeable computer scientists and software engineers for leadership and professional careers as well as for advanced study.
The programme produces highly qualified and motivated graduates through a rigorous curriculum of theoretical and applied knowledge that contributes to developing the ability to solve problems, individually, and in teams. Graduates of the programme are also provided interdisciplinary knowledge beyond the narrow disciplinary scope of computer science. Enabling them to be successful, ethical, and effective problem-solvers as well as life-long learners who can contribute positively to the economic well-being of the region, and prepared to tackle the complex challenges of the 21st Century. Graduates develop deep awareness of their ethical responsibilities to their profession and society at large.
The programme produces innovative leaders in the fields of computer science and software engineering.
As drivers of innovation in society, graduates will be at the forefront of innovative software development, advanced research, and dissemination of knowledge. The programme is implemented within the framework of an innovative research and teaching environment, which swiftly responds to the challenges of the 21st century. As such, it is expected to contribute to the production of quality human resources needed for the fast development of the IT industry in Central Asia.
The programme educates computer scientists and software engineers who can address the complex and diverse nature of Central Asian societies.
Graduates can become specialists in different areas of digital humanities contributing to the preservation and development of the rich cultural heritage of the region. Since various fields of digital humanities such as machine translation, computer linguistics, data analysis, data visualization, textual mining, and cultural analytics are located today in the vanguard of both computer applications and development of the humanities and social sciences, interdisciplinary educated computer science specialists are in high demand.
General Computer Science Capabilities:
Content-Specific Computer Science Capabilities:
A combination of different assessment methods is used to evaluate the performance of students in the Computer Science programme. Depending on the type of the course, they can be classified into two categories:
Faculty members assess student performance during instruction. This method usually occurs regularly throughout the instruction process and seeks to improve the achievement of students’ learning objectives through approaches that can support specific student needs. Examples of formative assessment methods used in the Computer Science programme include:
Faculty members evaluate students learning, knowledge, proficiency, or success at the conclusion of the instructional period. Summative assessments are always formally graded and can be used in conjunction and alignment with formative assessments. Examples of summative assessment methods used in the Computer Science programme include:

UCA's School of Arts and Sciences is pleased to announce that applications are open for the undergraduate programmes:
Undergraduate programmes:
- BSc in Computer Science (offered in Naryn, Kyrgyzstan)
- BA in Communications and Media (offered in Naryn, Kyrgyzstan)
- BSc in Earth and Environmental Sciences (offered in Khorog, Tajikistan)
- BA in Global Economics (offered in Khorog, Tajikistan)
All programmes are taught in English and follow an international curriculum emphasizing analytical thinking, research, and community engagement. UCA students benefit from small class sizes, personalized academic support, and extensive internship and career development opportunities.
Application deadline: 14 February 2026